Currently, on the market there are many companies specializing in manufacturing various Amplifier. Amplifier models but varied in texture and principle of operation, almost all of them in accordance with certain standards. Depending on the design firm handling circuit, the amplifier can operate in different modes such as Class A, AB, B, D, ….

Amplifier with many different types depending on the purpose for which the choice accordingly. At present, can be divided into the following categories Amplifier:
- Pre-Amplifier: This type Amplifier preamplifiers. It is responsible for signal amplification reminder from the source (DVD, DAC, ..) to a higher signal to power amplifier.

- Power Amplifier: Amplifier power is responsible for signal amplification from moderate to a large signal amplifier to the speakers.
- Integrated Amplifier: Integrated Amplifier block structured preamplifiers and power amplifiers block the same machine together.

- Dual Mono Amplifier: An integrated amplifier types have structural symmetry for two independent channels L & R separately (from the source to the amplifier section).

- Monoblock amply: Thiết kế khối tách biệt từng ampli cho mỗi kênh trái phải.

Although there are many different kinds of Amplifier but still following basic parameters:
- Power of Amplifier: amplifier power emitted is calculated in units of RMS (Root Mean Square). You need to distinguish the peak power PMPO (Peak Music Power Output) is much bigger than the capacity of the operation of the amplifier. PMPO is a term which manufactures audio equipment refers to the capacity of the largest sound output that their system can be achieved in a very short time, in the ideal conditions of laboratory but did not gain experience in actual use. Some manufacturers often advertise that PMPO huge capacity of up to thousands of W to attract users know little of the amplifier. Generally PMPO is an exaggerated term, does not mean anything apart from advertising, marketing. So you’re just interested in RMS power amplifier when looking to buy a certain kind.
- Power gain Amplifier: This is the ratio between the logarithm are input power and output power of the amplifier unit is dB. Said gain amplifier capable of great Amplifier will look like when the audio presentation.
- Frequency Response allows the Amplifier: Approximately frequency input signal that stable operation amplifier linearity. Usually good Amplifier frequency response from 20Hz to 20kHz in audio ear about who can smell. Frequency response as “flat” will demonstrate the capability of sound reproduction possible.
- Performance (Efficiency): Ability to make sound power according to the input power of the amplifier. When the electric power supply for the amplifier, only a fraction is amplified audio power output. The design principles Amplifier class A poor performing from 10% to 25% (that means when you supply power to 100W power amplifier 25W only sound is emitted), class AB performance 35 to 50%, while class D efficiency 85-90%.
- THD: total harmonic Comparing the frequencies between the input signal and output sound after passing Amplifier. The high harmonic distortion and reduces the fidelity of sound. So the lower the Amplifier THD as truthful sound reproduction, usually less than 0.5% THD right.
- Output Impedance: The impedance of the output amplifier to the loudspeaker. When paired with the impedance of the amplifier to the speaker, the speaker impedance usually halve the power amplifier should double if the coupling impedance difference.
Amplifier can be operated in different modes such as Class A, AB, B, D … Depending on circuit design principles. Some basic circuit types commonly used today are Class A and Class AB Single-End Push-Pull.
- Class A Single End
Designed for low efficiency is only about 25% (ie if 100W input power supply only 25W of output power in speakers, 75W with losses as oysters or heat on electronic lamp while performance Class AB 35 to 50% (100W 50W input to the speaker output). Therefore, the size and cost of the problem for oysters capacity radiator of ClassA and hence larger than ClassAB. The work located at the midpoint of the load curve. At the point load characteristics of the input signal is amplified 100% and just one scallop was undertaken this work. So called single-end (SE).
Advantages of Single-End Amplifier ClassA is no nonlinear domain (nonlinearities) and radial distortion (cross distortion, turn on / off delay) by only a single oyster operation. ClassA audio amplifiers which are considered sweet and truthful. A further point to note is that the amplifier is called “pure” A (pure ClassA) will operate completely in mode A. Note that some amplifiers with advertisers ClassA but merely operate in mode A domain in moped, when the amplifier was operational requirements for a large capacity of work will switch to AB.

- Class AB Push-Pull
Push-pull design (push-pull) of high-efficiency Class AB output power to the large speakers. The problem is that the push-pull amplifier has worked in the region point stop (cutoff) of the load curve. At this cutoff point work only 50% of the input signal is amplified, so you have to use two operating power scallops, oysters will amplify a signal part positive and some negative signal amplifying section ( push-pull), so called Push-Pull. Advantages of Push-Pull Class AB under evaluation is common space, monumental and the fine.
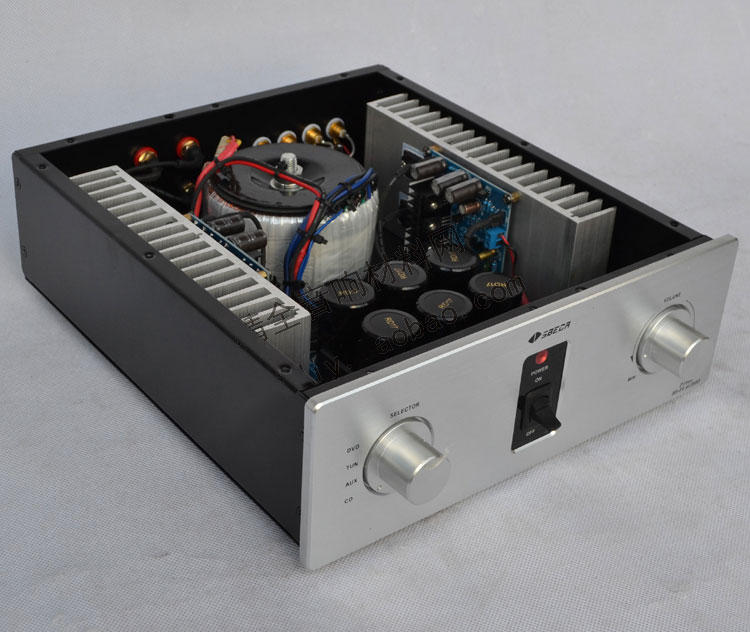

Amplifier class AB
- Class B
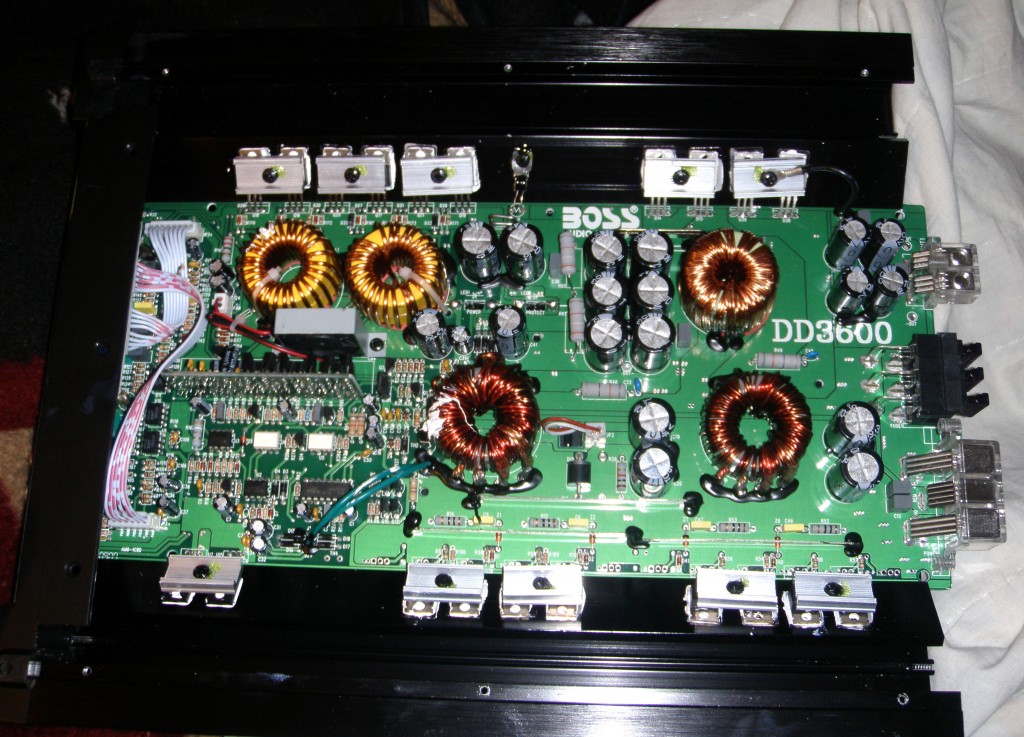
- Class D

Phan Nguyễn Audio cung cấp cho bạn một số kiến thức cơ bản về Amply. Nếu có thắc mắc vui lòng liên hệ chúng tôi.
Incoming search terms:
- cau tao amply
- cau tao va nguyen ly hoat dong cua amply



